Digital Infra-red Thermal Imaging (DITI)
What is Digital Infra-red Thermal Imaging (DITI)?
Digital Infra-red Thermal Imaging (DITI) is a unique heat-seeking clinical imaging technique that records the thermal patterns of your body. It detects the physiological changes in your body, such as patterns of blood flow, vascular changes, inflammation and asymmetries. Other screening tools like MRI and X-ray can only detect anatomical changes so will miss such things as active inflammation or angiogenesis (increased blood supply as found in cancer). Inflammation, as characterized by several familiar signs such as redness, swelling, heat and pain, is the first sign of serious diseases like cancer, heart disease, stroke, arthritis and others. Thus, DITI can detect early danger signs in the body years before other tools without any emission of harmful radiation.
DITI is used as an aid for diagnosis and monitoring pain or pathology in any part of your body. It is useful for the conditions and injuries including:
|
|
|
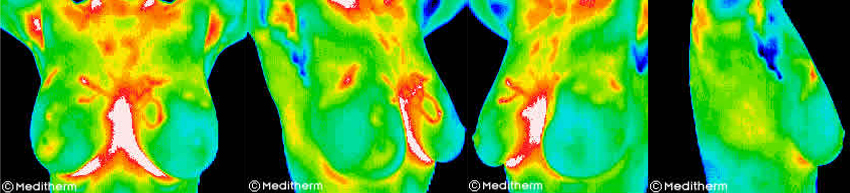
A ‘Do No Harm’ approach to breast screening
Digital Infra-red Thermal Imaging (DITI) is approved by the FDA for breast cancer screening in 1982. It can detect the subtle physiologic changes that accompany breast pathology, whether it is cancer, fibrocystic disease, an infection or a vascular disease.
The benefit of DITI scaning is that it offers the opportunity of earlier detection of breast disease than it would have been possible through self-examination, doctor examination or mammography alone. DITI has been shown to be effective in finding early signs of breast cancer up to 8 years before the mammogram.
Some facts about Mammogram Screening
- Mammogram screening can only detect at least 1 cm-sized tumour. Most tumours take about 8 to 10 years to grow to 1 cm in size. Thus, mammogram screening might miss a tumour until after it has been growing for years to a sufficient size for detection.
- Mammogram screening uses ionizing radiation, a known cancer-causing agent which can cause irreparable damage to the DNA. The radiation exposure from a mammogram screening is not similar to that from a chest X-ray. A mammogram screening which involves taking 4 films of each breast delivers 1 rad exposure. The amount seems trivial but it is in fact 1000 times greater than that from a chest X-ray. Thus, mammogram radiation is much more damaging than a chest X-ray and it poses significant and cumulative effect on body by increasing the risk of breast cancer.
- Mammogram screening entails tight compression of breast which causes discomfort and blatant pain in most women. What is worse is the tight and painful compression may rupture the small blood vessels and dislocate the existing yet undetected malignant cells, lead to lethal spread of cancer. For breast implants women, there is a slim chance of implants rupture during the tight compression. Moreover, the implants will obscure the images makes the mammogram interpretation more difficult.
- The overall sensitivity of mammography is about 80% – 85% but the value is lower among the young women and women with dense breast tissue. Mammogram images of women under the age of 40 and those with dense breast tissue are especially difficult to read and it leads to higher chance of false-positive result. Mistakenly diagnosed cancer undoubtedly brings unnecessary biopsies and psychological stress to them.
Well noted on the major shortcomings of mammogram, several alternative technologies have been invented to overcome these limitations. One of the alternative technologies is Digital Infra-red Thermal Imaging, DITI. All women can benefit from DITI breast screening. However, it is especially appropriate for younger women (30 – 50 years old) whose denser breast tissue, fibrocystic breasts, implants or those who had mastectomies without reconstructive surgery. Results in fewer unnecessary biopsies especially for women with dense and fibrocystic tissue.
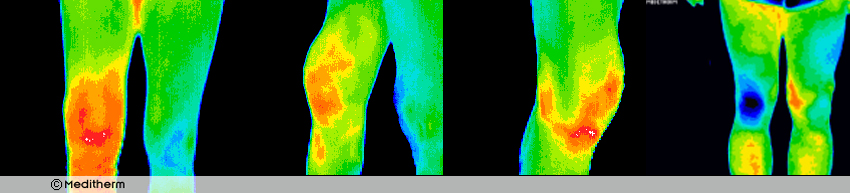
‘Visualising’ your pain. Taking the guesswork out of clinical pain assessment
Clinical assessments are usually difficult due to the subjective patient’s description of their sensations. DITI yields objective results. Thus, reliance on patient’s subjective reporting is far lessened and the practitioner is able to better understand and scale the reported symptoms.
Pain can arise from inflammatory conditions like arthritis, soft tissue injuries or from vasomotive conditions like Complex Regional Pain Syndrome where damaged nerves can no longer control the blood flow, sensation, temperature to affected area. DITI has a good chance of differentiating localised joint pain, sympathetic irritation and other more widespread inflammation indicative of a separate infection or condition.